云与虚拟化_实验7 Docker网络管理应用
实验要求
了解Docker常用网络模式,掌握Docker常用网络模式的使用。本实验主要任务是利用busybox镜像建立容器,容器名称为test_busybox1和test_busybox2,将网络模式设置为none,并为容器配置IP地址,容器test_busybox1的IP设置为172.17.0.100,容器test_busybox2的IP设置为172.17.0.200,要求实现两容器互通。
前置准备
要求实验主机能够连接外网,已经正确安装Docker,并关闭防火墙和selinux。
实验过程
步骤1-3
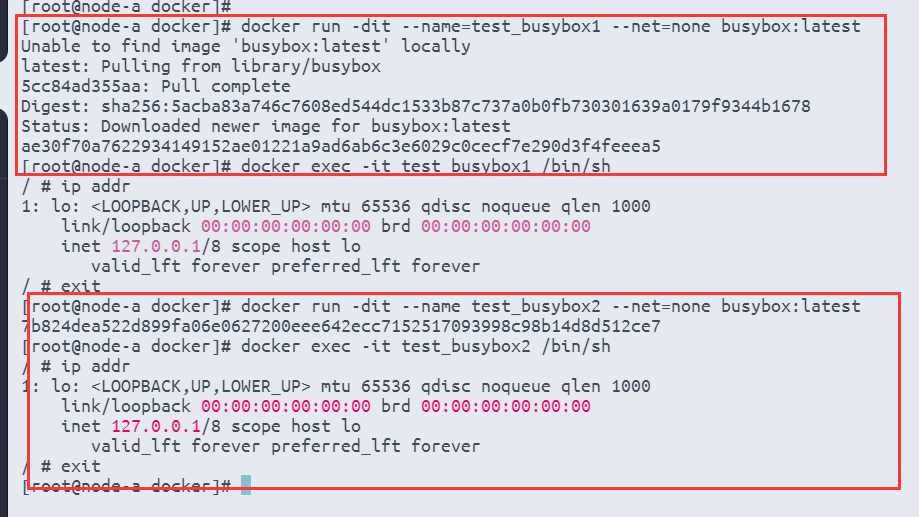
# 步骤1.1: 创建容器test_busybox1,设置网络模式为none
docker run -dit --name=test_busybox1 --net=none busybox:latest
# 进入容器test_busybox1
docker exec -it test_busybox1 /bin/sh
# 步骤1.2: 查看IP地址(容器test_busybox1)
ip addr
# 从现象可以得知容器test_busybox1没有IP地址。
# 退出容器test_busybox1
exit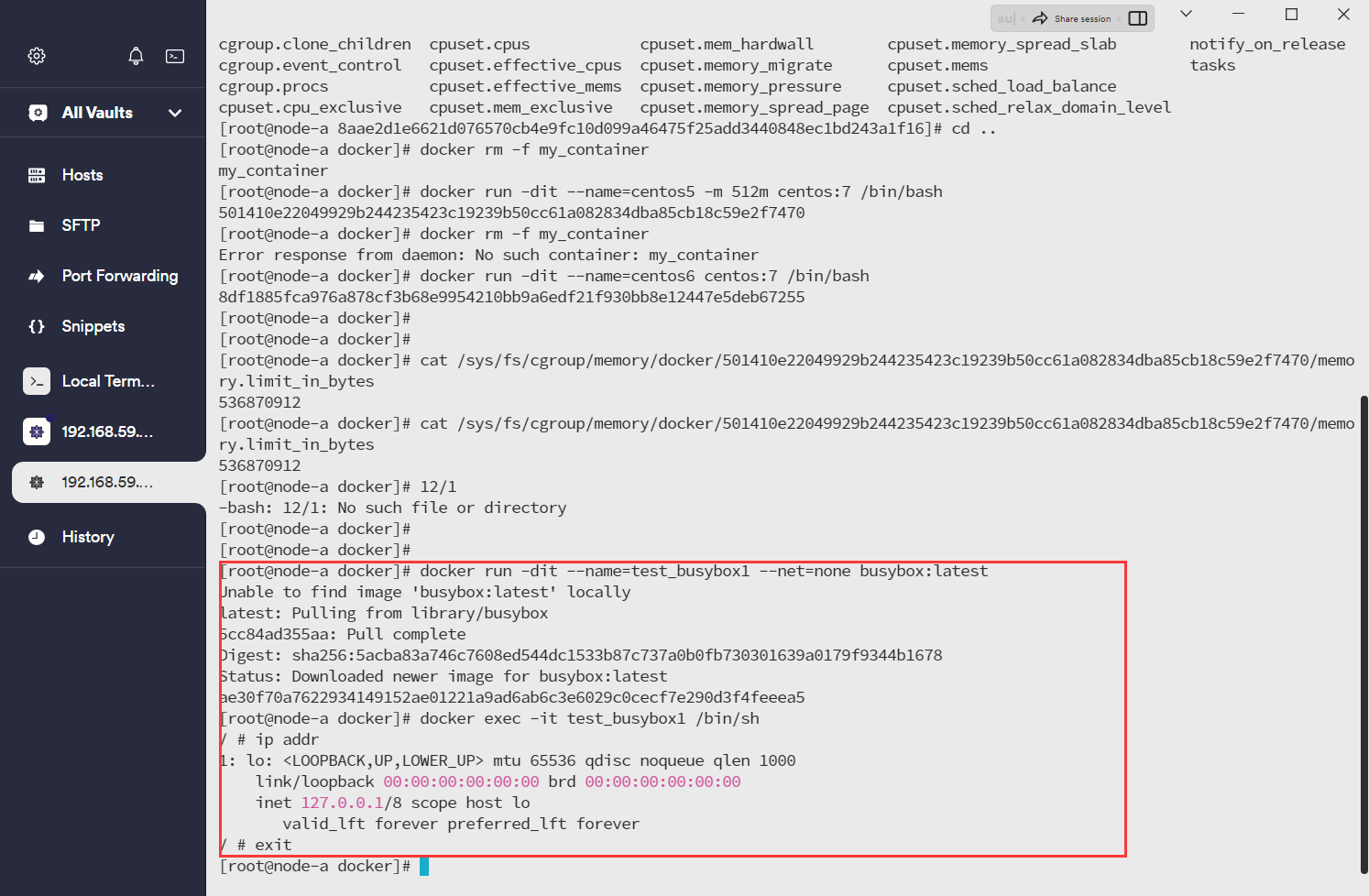
# 步骤2.1: 创建容器test_busybox2,设置网络模式为none
docker run -dit --name test_busybox2 --net=none busybox:latest
# 进入容器test_busybox2
docker exec -it test_busybox2 /bin/sh
# 步骤2.2: 查看IP地址(容器test_busybox2)
ip address
# 退出容器test_busybox2
exit从现象可以得知容器test_busybox1,test_busybox2都没有IP地址。
步骤4
# 步骤3: 为容器test_busybox1设置IP地址为172.17.0.100
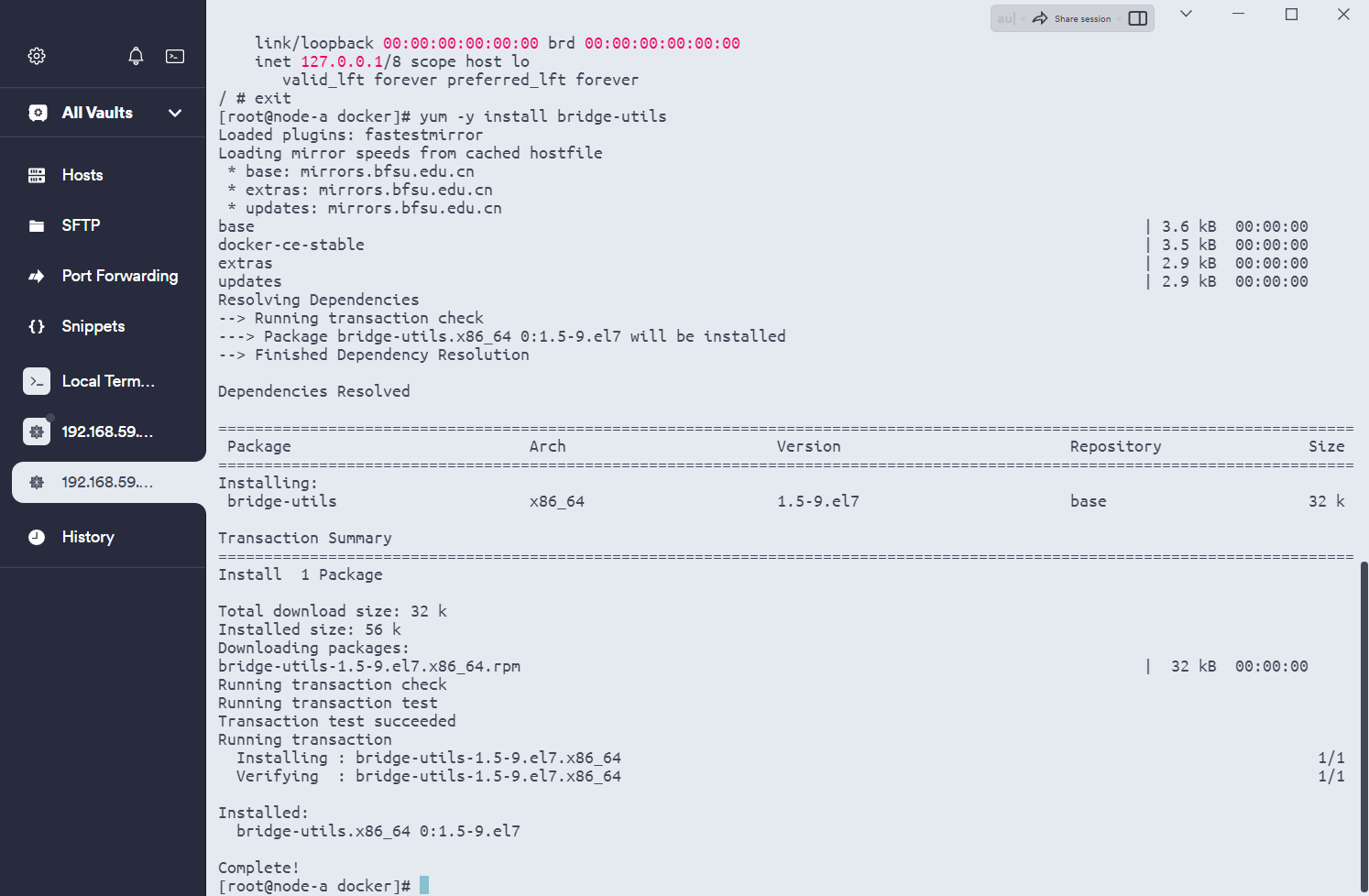
# 安装bridge-utils软件包
yum -y install bridge-utils
# 创建veth对,并将veth0加入docker0网桥
ip link add veth0 type veth peer name veth1
# 虚拟网桥 peer的name
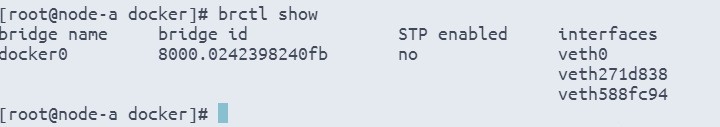
brctl addif docker0 veth0
# 桥接管理器 添加 管理桥接
brctl show
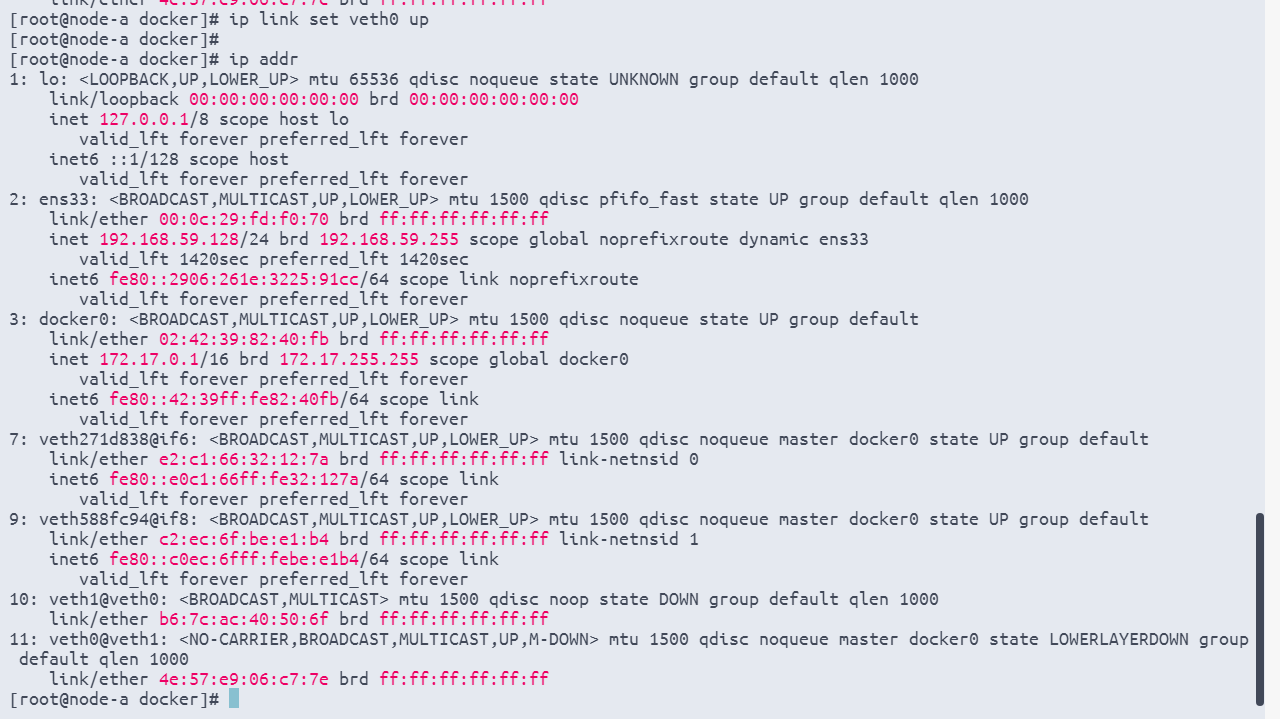
# 启动veth0,原神启动 (另外一个veth1也会自动启动)
ip link set veth0 up
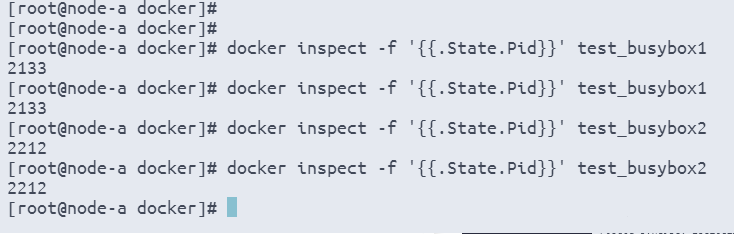
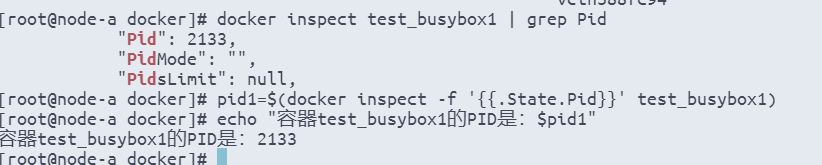
# 获取容器test_busybox1的PID
pid1=$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Pid}}' test_busybox1)
echo "容器test_busybox1的PID是:$pid1"
#有两种途径索引network namespace:名字(例如netns1)或者属于该namespace的进程PID。
#使用命名(Name):为网络命名空间分配可读的名称,然后使用该名称来引用和操作命名空间。这使得管理网络命名空间更加方便和直观。
#使用进程PID:每个网络命名空间都与一个进程相关联,通常是一个子进程。可以使用该进程的PID来访问和管理与之关联的网络命名空间。
# 创建network namespace软连接
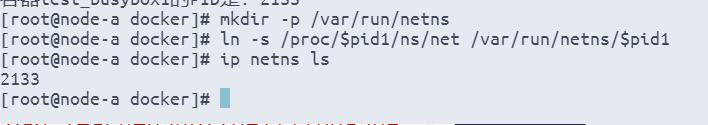
mkdir -p /var/run/netns
ln -s /proc/$pid1/ns/net /var/run/netns/$pid1
ip netns ls
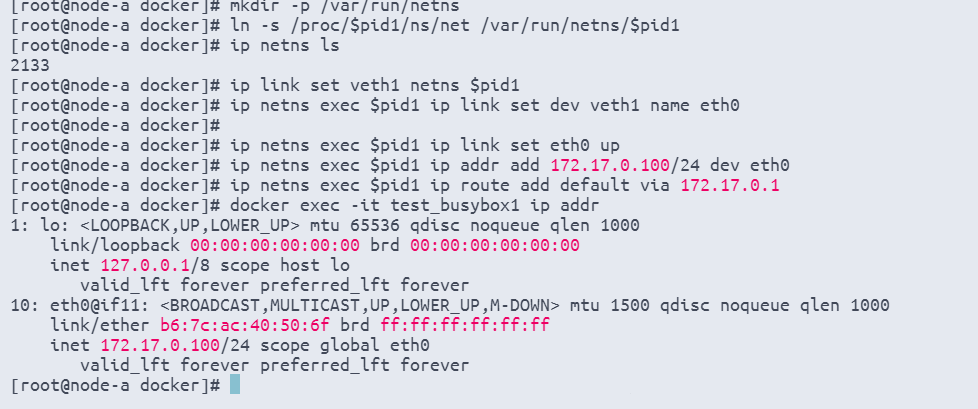
# 将veth1连接到容器test_busybox1的network namespace,并重命名为eth0
ip link set veth1 netns $pid1
ip netns exec $pid1 ip link set dev veth1 name eth0
# 启用eth0
ip netns exec $pid1 ip link set eth0 up
# 分配IP地址和设置网关
ip netns exec $pid1 ip addr add 172.17.0.100/24 dev eth0
ip netns exec $pid1 ip route add default via 172.17.0.1安装包:
网桥:
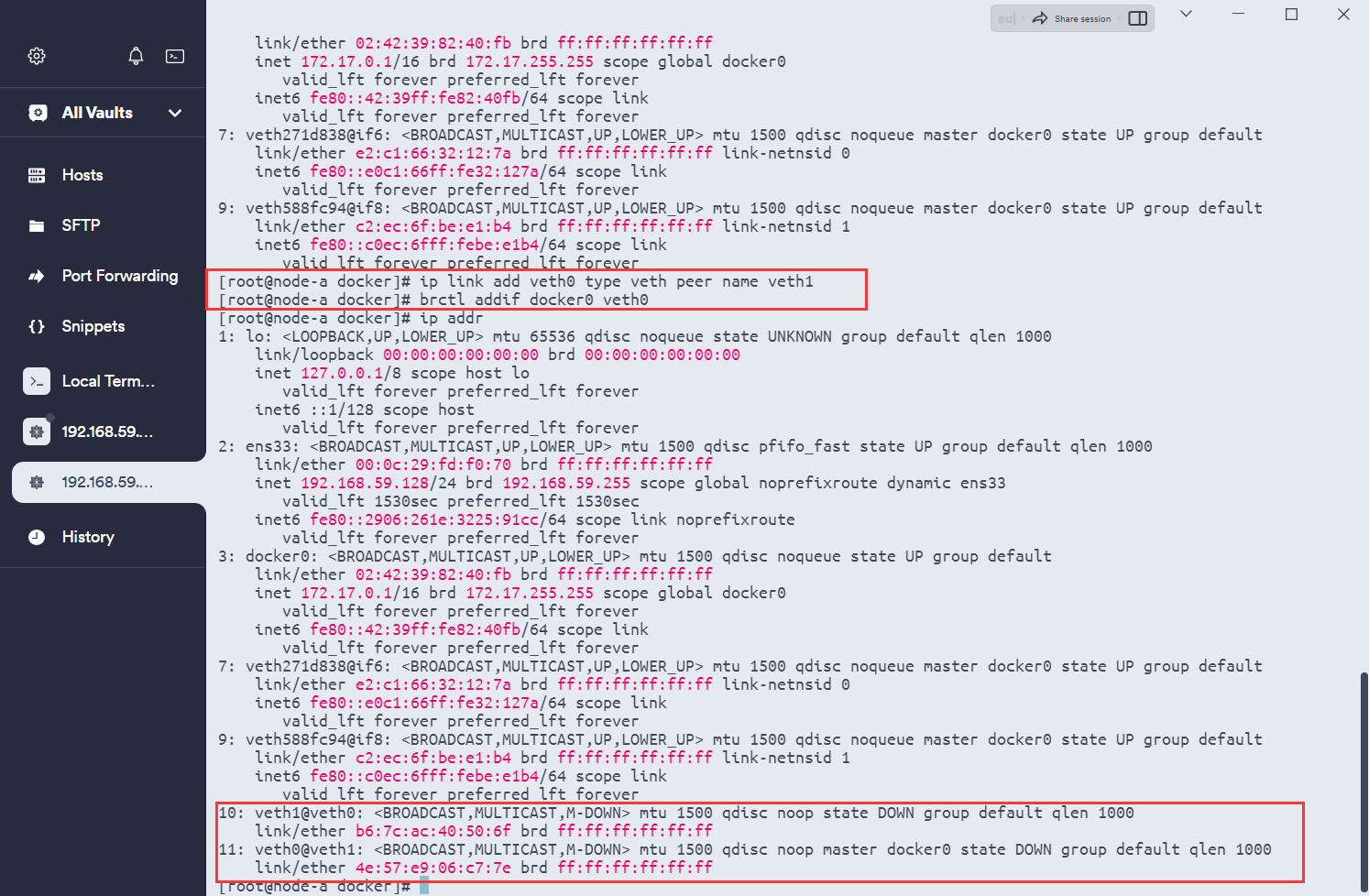
veth0启动:
PID:
Docker State信息
-
.Id: 容器的唯一标识符,通常是一个长字符串,也被称为容器ID。 -
.Name: 容器的名称,通常是用户定义的名称,可以用来引用容器。 -
.State.Status: 容器的状态,如运行中、停止等。 -
.State.Running: 表示容器是否正在运行(布尔值)。 -
.State.Pid: 容器内部主进程的PID。 -
.Config.Image: 使用的容器镜像的名称。 -
.Config.Cmd: 启动容器时使用的命令。 -
.Config.Env: 容器的环境变量。 -
.NetworkSettings.IPAddress: 容器的IP地址(如果有网络配置)。 -
.HostConfig.Binds: 挂载到容器内部的卷或目录。 -
.Mounts: 容器的挂载点信息。 -
.Created: 容器创建的时间戳。 -
.Ports: 容器的端口映射信息。 -
.Labels: 用户定义的容器标签。 -
.LogPath: 容器的日志文件路径。 -
.HostConfig.NetworkMode: 容器的网络模式。
netns:
执行完之后,可以看到已经分配到网卡:
目前这个namespace叫2133
然后再命名空间里执行了一些命令。
步骤5
配置容器test_busybox2的网络
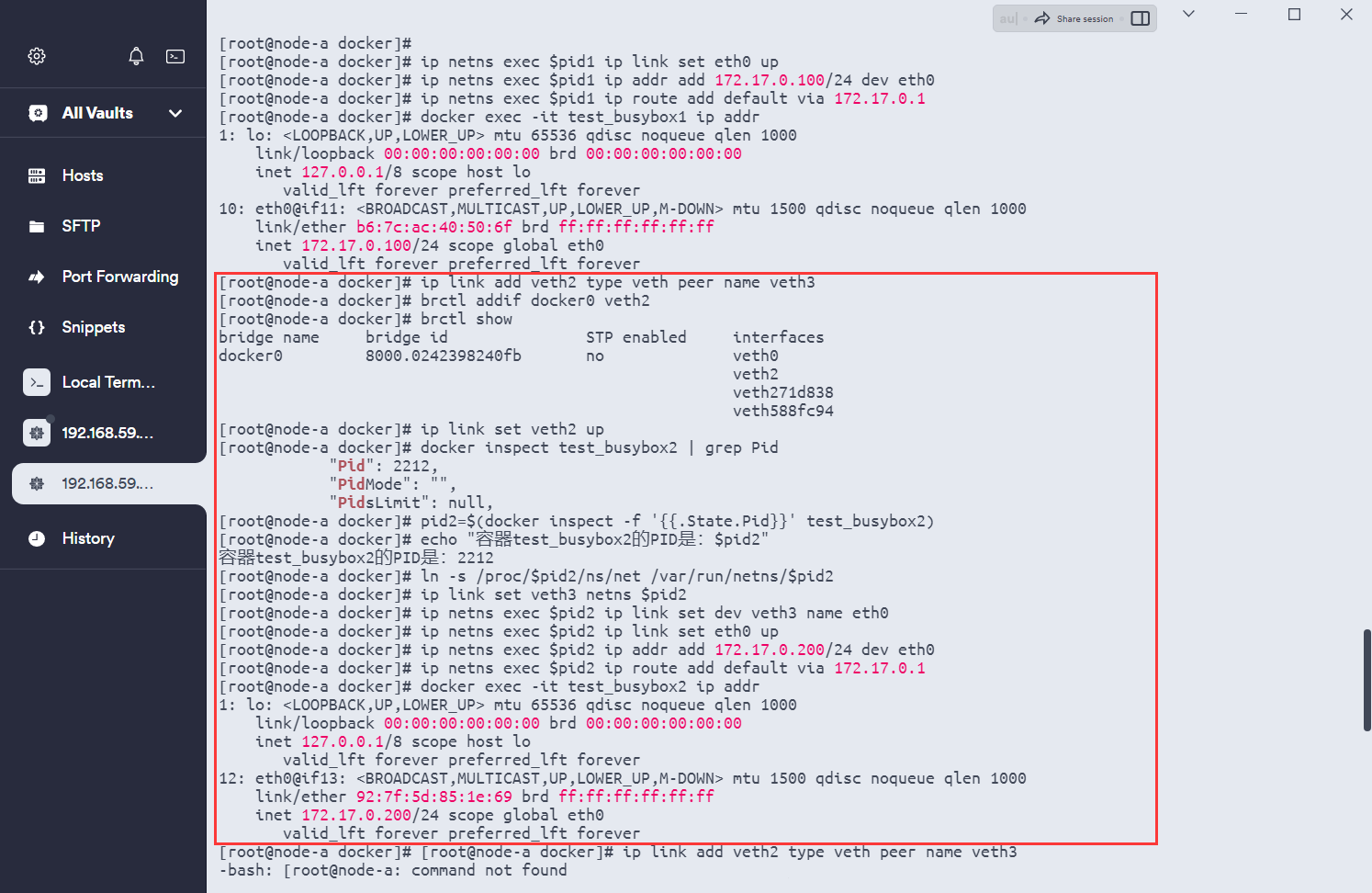
# 创建一对虚拟以太网设备veth2和veth3,这两个设备是成对出现的,数据可以在两个设备之间传送
ip link add veth2 type veth peer name veth3
# 将veth2这端加入到docker0桥接器中,这样veth2就能和docker0桥接器上的其他网络设备进行通信了
brctl addif docker0 veth2
# 显示当前桥接器的信息,可以看到docker0桥接器及其所连接的网络接口
brctl show
# 启用veth2网络接口,使其能够进行数据传输
ip link set veth2 up
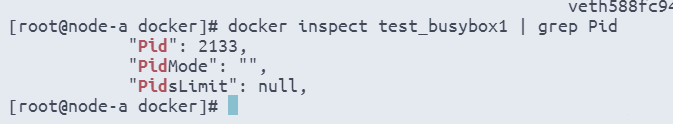
# 使用docker命令检查名为test_busybox2的容器,提取容器的进程ID
docker inspect test_busybox2 | grep Pid
# 用docker inspect命令获取名为test_busybox2的容器的PID,并将其存储在变量pid2中
pid2=$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Pid}}' test_busybox2)
# 输出容器test_busybox2的PID
echo "容器test_busybox2的PID是:$pid2"
# 为容器的网络命名空间创建一个软链接,方便后续的操作。/var/run/netns/目录通常用于存放网络命名空间
ln -s /proc/$pid2/ns/net /var/run/netns/$pid2
# 将veth3这端的网络接口移到容器test_busybox1的网络命名空间中
ip link set veth3 netns $pid2
# 在test_busybox1容器的网络命名空间内,将网络接口veth3重命名为eth0
ip netns exec $pid2 ip link set dev veth3 name eth0
# 启用容器内的eth0网络接口
ip netns exec $pid2 ip link set eth0 up
# 为容器内的eth0接口分配IP地址172.17.0.200,并设置子网掩码为24位
ip netns exec $pid2 ip addr add 172.17.0.200/24 dev eth0
# 设置容器内的网络路由,使其默认网关为172.17.0.1,即docker0桥的IP地址
ip netns exec $pid2 ip route add default via 172.17.0.1
[root@node-a docker]# ip link add veth2 type veth peer name veth3
[root@node-a docker]# brctl addif docker0 veth2
[root@node-a docker]# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
docker0 8000.0242398240fb no veth0
veth2
veth271d838
veth588fc94
[root@node-a docker]# ip link set veth2 up
[root@node-a docker]# docker inspect test_busybox2 | grep Pid
"Pid": 2212,
"PidMode": "",
"PidsLimit": null,
[root@node-a docker]# pid2=$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Pid}}' test_busybox2)
[root@node-a docker]# echo "容器test_busybox2的PID是:$pid2"
容器test_busybox2的PID是:2212
[root@node-a docker]# ln -s /proc/$pid2/ns/net /var/run/netns/$pid2
[root@node-a docker]# ip link set veth3 netns $pid2
[root@node-a docker]# ip netns exec $pid2 ip link set dev veth3 name eth0
[root@node-a docker]# ip netns exec $pid2 ip link set eth0 up
[root@node-a docker]# ip netns exec $pid2 ip addr add 172.17.0.200/24 dev eth0
[root@node-a docker]# ip netns exec $pid2 ip route add default via 172.17.0.1
[root@node-a docker]# docker exec -it test_busybox2 ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
12: eth0@if13: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP,M-DOWN> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue qlen 1000
link/ether 92:7f:5d:85:1e:69 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.200/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@node-a docker]#步骤6:测试
docker exec -it test_busybox2 ip addr
docker exec -it test_busybox2 ping -c 4 172.17.0.100docker exec -it test_busybox1 ip addr
docker exec -it test_busybox1 ping -c 4 172.17.0.200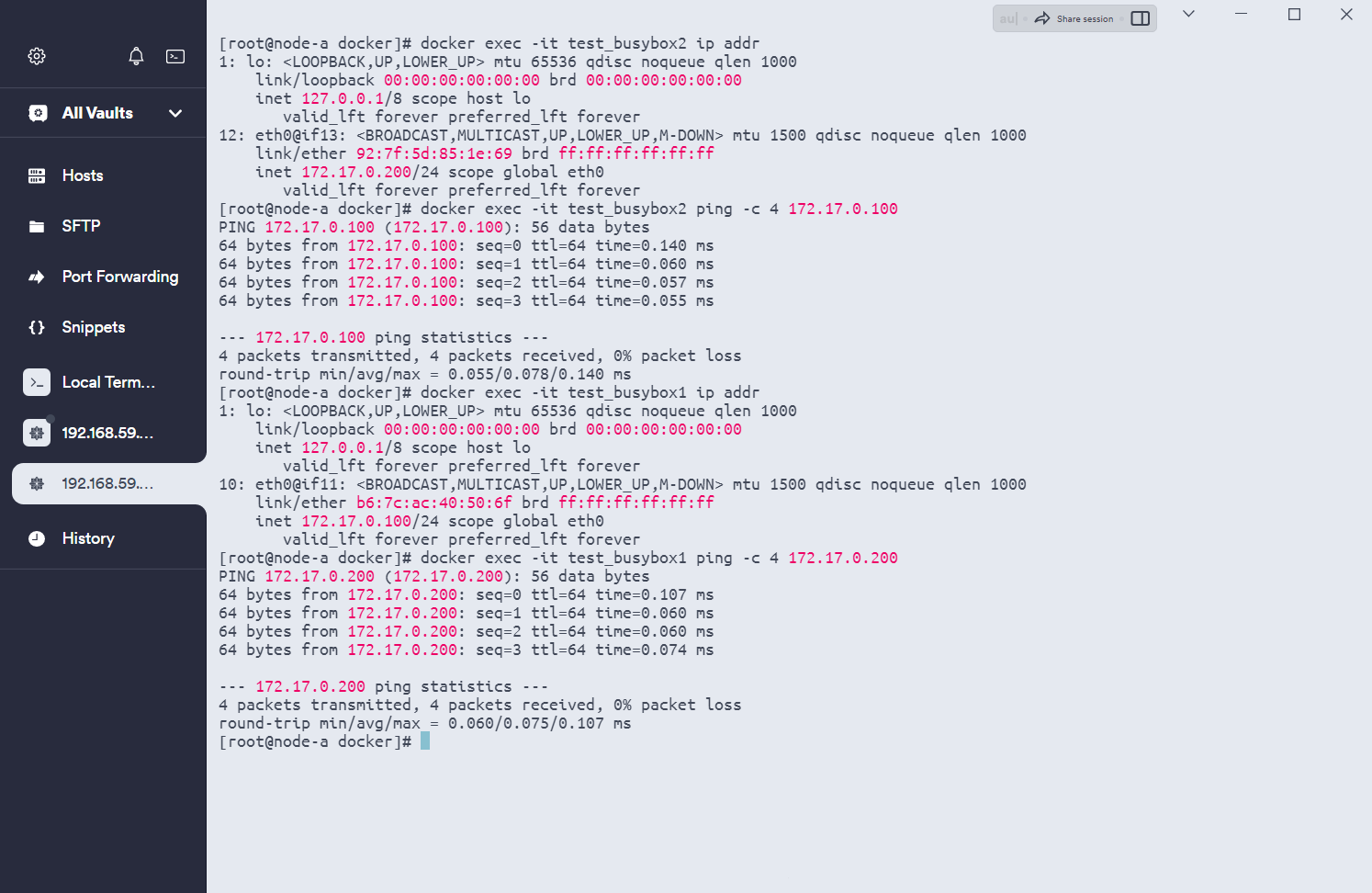
发表回复